
SMPTE ST 428-1 Image Characteristics specifies two classes of picture resolution: 2K and 4K. For each class of resolution, the standard defines the available container for the picture, as shown in the table below.
| Resolution | Maximum Horizontal Pixels | Maximum Vertical Pixels |
| 4K | 4096 | 2160 |
| 2K | 2048 | 1080 |
Table P-1. Picture Containers
Theoretically, any aspect ratio can be carried in the container, so long as the maximum horizontal or vertical pixel count is not exceeded. In practice, however, cinemas are set up to support only two aspect ratios. The “scope “aspect ratio, which is 2.39:1, is centered in the container with maximum width. The “flat” aspect ratio, which is 1.85:1, is centered in the container with maximum height. The image sizes for scope and flat aspect ratios are shown in the table below.
| Resolution | Aspect Ratio | Horizontal Pixels | Vertical Pixels |
| 4K | Scope 2.39:1 | 4096 | 1716 |
| 4K | Flat 1.85:1 | 3996 | 2160 |
| 2K | Scope 2.39:1 | 2048 | 858 |
| 2K | Flat 1.85:1 | 1998 | 1080 |
Table P-2. Picture Resolutions
Resolution is recognized as an important quality of digital images. But the human perception of resolution is limited by visual acuity. Good vision is defined as that capable of discerning an object at a visual angle of 1 arc minute, or 1/60 of a degree. Using this information, the required seating position in relation to the screen can be calculated for discerning one pixel, as illustrated in the diagram below.
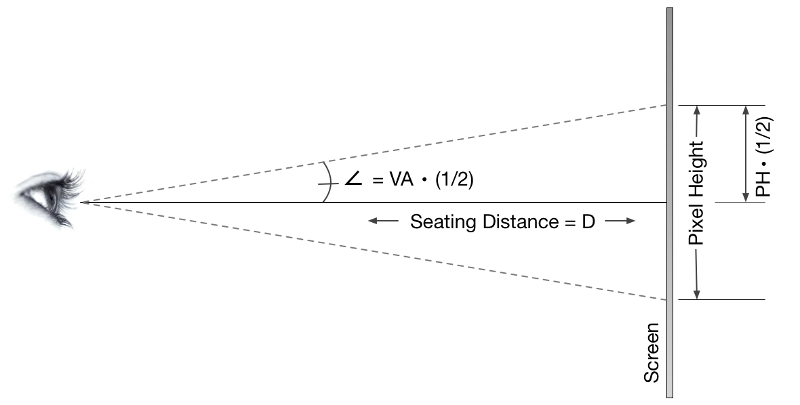
Figure P-6. Visual Acuity and Resolution
Applying trigonometry, the following equation can be derived:
tan (VA * 1/2) = PH / 2D
Where
- D = seating Distance (or viewing distance)
- PH = Pixel Height
- VA = Visual Angle = 1/60 or 0.000145444 degree.
In cinema, seating position is often referenced in terms of picture height, recognizing the geometrical relationship of seating position to screen. From the charts above, picture height of a 4K image is at most 2160 pixels. One pixel height, therefore, would be 1/2160 screen height.
Taking this into account, the formula for maximum viewing distance D is:
D = [1 /(2 * 2160)] / [ tan (VA * 1/2)]
Using this equation, D = 1.59 screen heights. In other words, the furthest seating position where a 4K image can be appreciated in full resolution is 1.59 screen heights from the screen. For a 2K image, the distance is twice that. To give this perspective, most cinemas place seats nearest the screen around the 1 screen height position. This leaves only a few rows where 4K resolution can be fully appreciated.
There is also audience preference to consider. The audience tends to prefer seating in the middle of the auditorium and not the front of the auditorium, where mid-auditorium is typically around 3 screen heights from the screen. The paradox of higher resolution imagery in cinema is that the seats that benefit most from higher resolution are not the seats that the audience values.